this post was submitted on 22 Dec 2025
360 points (98.9% liked)
Greentext
7648 readers
253 users here now
This is a place to share greentexts and witness the confounding life of Anon. If you're new to the Greentext community, think of it as a sort of zoo with Anon as the main attraction.
Be warned:
- Anon is often crazy.
- Anon is often depressed.
- Anon frequently shares thoughts that are immature, offensive, or incomprehensible.
If you find yourself getting angry (or god forbid, agreeing) with something Anon has said, you might be doing it wrong.
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
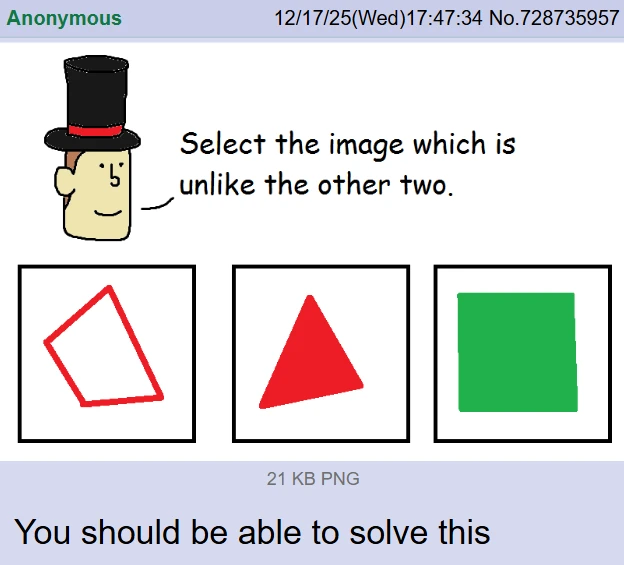
No.
You are wrong.
"Select the image that is unlike the other two."
The only possible choice that results in a set of 2, and a set of 1, which are seperated cleanly by a distinct property, is picking C.
The goal is to define a difference between potential sets such that a distinct property exists between the two sets that you create.
To define two sets where unlikeness exists between them when they are compared.
Your job is not to merely compare three elements.
It is to compare three possible pairs of sets that can be made out of three elements.
Which elements have which particular combinations of attributes is thus very important, not irrelevant, as your simplified description of the situation portrays.
And that's literally what they did.
There's a set of shapes that are filled, and a distinct set of one that is outline only.
There's a set of shapes that have 4 sides, and a distinct set of one that is 3 sides only.
There's a set of shapes that are red, and a distinct set of one shape that is green.
Only when you pick C do you result in a pair of sets that are cleanly dvided by the same property difference.
Is that more clear?
If you pick C, the distinction between C and A is the same distinction between C and B.
Thus, if you pick C, C is unlike A and B in the same way.
This is what I would call a clean or clear distinction, or ... kind of unlikeness.
This is not the case, does not occur, if you pick A or B.
You end up with a picked set of one element that differs from the remainder set in ways that are inconsistent among the elements of the remainder set.
IE, a muddled or inconsistent distinction.
I think you are overthinking this mate.
I concur, and realized my logic is flawed.
... sorry.