this post was submitted on 15 Nov 2024
821 points (99.3% liked)
Linux
63358 readers
869 users here now
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Linux is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991 by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged in a Linux distribution (or distro for short).
Distributions include the Linux kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name GNU/Linux to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy.
Rules
- Posts must be relevant to operating systems running the Linux kernel. GNU/Linux or otherwise.
- No misinformation
- No NSFW content
- No hate speech, bigotry, etc
Related Communities
Community icon by Alpár-Etele Méder, licensed under CC BY 3.0
founded 6 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
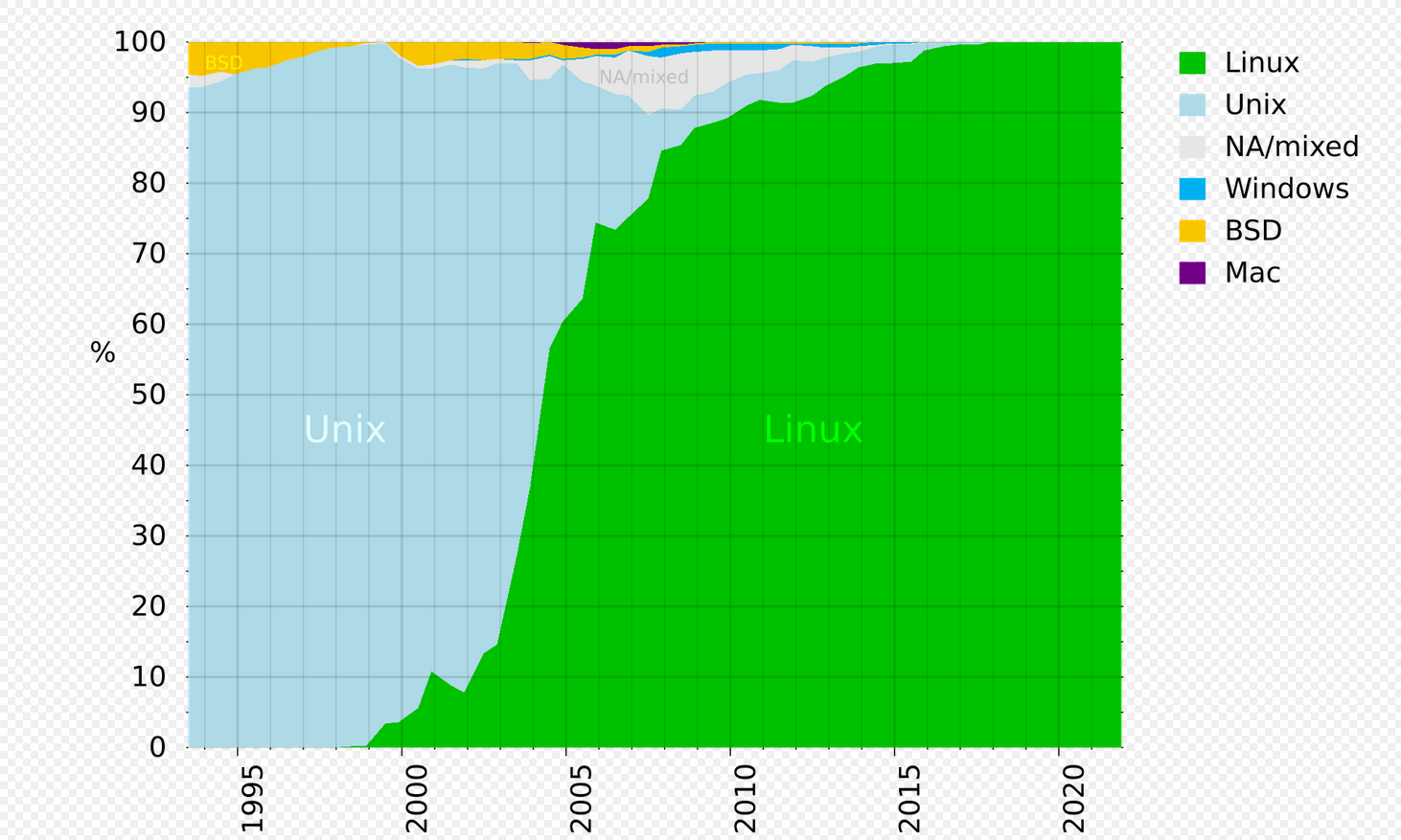
I’m confused on why they separate BSD from Unix. BSD is a Unix variant.
Unix is basically a brand name.
BSD had to be completely re-written to remove all Unix code, so it could be published under a free license.
It isn't Unix certified.
So it is Unix-derived, but not currently a Unix system (which is a completely meaningless term anyway).
But OS X, macOS, and at least one Linux distro are/were UNIX certified.
Yup. It is all about paying the price, Microsoft could technically get Windows certified as UNIX. IBM did just that with its mainframe OS. Here's a list of certified UNIX systems: https://www.opengroup.org/openbrand/register/
I don't think they could now that the POSIX subsystem and Windows Services for UNIX are both gone. Don't you need at least some level of POSIX compliance (at least the parts where POSIX and Unix standards overlap) to get Unix certified?
It means nothing, it's just a paycheck you sign and then you get to say "I certify my OS is Unix". The little bit more technical part is POSIX compliance but modern OSs are such massive and complex beasts today that those compliances are tiny parts and very slowly but very surely becoming irrelevant over time.
Apple made OSX Unix certified because it was cheap and it got them off the hook from a lawsuit. That's it.
To make it more specific I guess, what's the problem with that? It's like having a "people living on boats" and "people with no long term address". You could include the former in the latter, but then you are just conveying less information.
Others have answered, but it is interesting to know the history of UNIX and why this came to be. BSD is technically UNIX derived, but being more specific isn't the reason why it has distinct branding. As with many evils the root is money, and there's a lot in play into how it all happened, including AT&T being a phone monopoly.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/UNIX_System_Laboratories,_Inc._v._Berkeley_Software_Design,_Inc.
And I recommend watching this video informative and funny about the history and drama behind it all: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g7tvI6JCXD0
So is Linux. So I guess the light blue is all other UNIX variants?
I think this is a Ship of Theseus thing here that we're going to argue about because at what point is it just UNIX-like and not UNIX?
UNIX-like is definitely a descriptor currently used for Linux.
Even the Wikipedia entry starts that way.
Yes, but it's not Unix. That's literally part of GNU/Linux' name.
Mac OS is more Unix than Linux.
It's Unix if you pay to have it certified (assuming it's compatible to begin with). That's basically it.
Some Linux distros have
Some commercial ones did at some point. I'm not sure if they still do.
The question is whether their users care or not I suppose.
EulerOS, a Linux distro, was certified UNIX.